Have you ever had a last-minute panic before an audit because you couldn’t find a document or weren’t sure which version was approved? It must be incredibly stressful to go through this.
This kind of scenario is actually not uncommon. According to a study by Adobe, 71% of employees report that poor digital organization hinders their ability to work effectively. Common issues include difficulties in finding documents quickly, inconsistent naming conventions, and a lack of access control. To address these challenges, your organization requires proper document control, typically supported by document control software that organizes, tracks, and secures documents.
In this guide, we’ll break down what document control is, its core components, why it’s important, how to implement it effectively, and examples of document control in different industries.
Capture Key Data from Your Documents Easily
Use Docparser to automate data entry, save time, and streamline your document-based workflows.
No credit card required.
What Is Document Control?
Document control is the practice of systematically managing documents to keep them organized, accessible to the right people, and secure. In practice, it sets a clear protocol for creating, reviewing, approving, distributing, and maintaining documents throughout their lifecycle.
The goal of document control is to ensure that the right information is available to the right people at the right time. To that end, documents must be:
- Accurate
- Approved
- Up to date
- Traceable
- Stored securely
- Accessible only to authorized users
- Compliant
- Audit-ready
Without proper document control, teams (and external parties) struggle with outdated versions, missing approvals, workflow inefficiencies, and slow retrieval during audits or reviews.
All these problems can be avoided by having a strong document control system in place. This becomes particularly important in environments where compliance, traceability, and consistency are critical. Furthermore, obtaining certification, like ISO 9001, requires having a document control system.
What a document control process looks like
Document control applies a standardized process to documents within an organization that require control. This process covers the stages in a document’s lifecycle. Here is what it looks like:
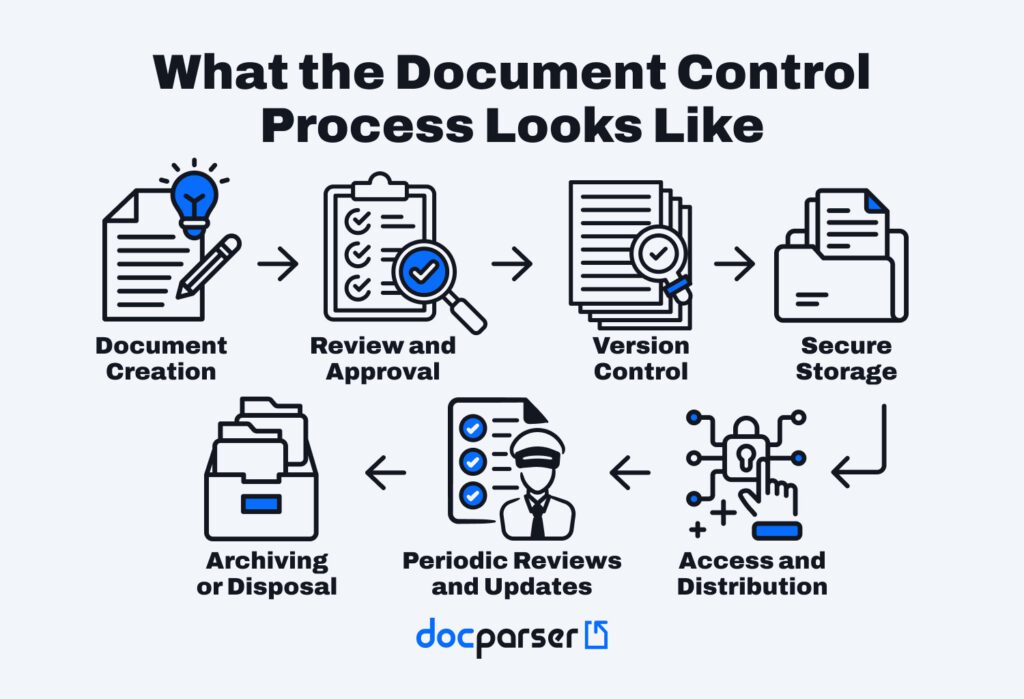
Let’s break each step down:
- Document creation: a person creates a draft of a document. The contents may go through multiple revisions.
- Review and approval: a document approver reviews the draft, requests changes if necessary, and approves it. The approved version is now ready for official use.
- Version control: each new version of the document is assigned a version identifier and logged. Document version control ensures that employees use the current version and keep a history of versions.
- Secure storage: documents are stored in a secure and centralized system that prevents unauthorized access and facilitates retrieval.
- Access and distribution: a document control specialist manages access permissions and distributes approved documents to authorized stakeholders.
- Periodic reviews and updates: documents are reviewed at scheduled intervals to ensure they remain accurate and compliant with regulations or internal policies. Updates go through the same review and approval process.
- Archiving or disposal: documents that are no longer active or required get either archived for record-keeping or securely disposed of as per retention policies.
Each step ensures that documents move forward in a controlled way, reducing the risk of errors, duplication, or unauthorized changes.
What documents need to be controlled?
Not every single document in an organization needs control. For example, it’s not necessary to control informal emails or short-term checklists.
As a rule of thumb, any document related to quality management, operations, compliance, or decision-making should be controlled. Common examples include:
- Policies and procedures
- Contracts and legal documents
- Invoices, purchase orders, and financial records
- Technical documentation and specifications
- Compliance, quality, and audit-related records
If a document needs to be accurate, traceable, or auditable, it belongs in a document control system.
Document control vs document management: what’s the difference?
Those two terms are related to each other, so you might wonder how they’re different from each other.
Document management focuses on storing, organizing, and retrieving documents efficiently. Furthermore, document management systems (DMS for short) often include functions such as document versioning and integrations with collaboration tools.
But here is the difference: document control goes further than storing and sharing documents. It oversees the entire document lifecycle and enforces compliance.
There is an overlap between the two, specifically functions such as centralized storage, search and retrieval, and basic access permissions.
However, document control includes functions that are outside the scope of document management:
- Advanced document versioning and revision tracking
- Formal procedures for document reviews and approvals
- Strict access and editing controls
- Controlled distribution
- Retention and disposal policies
- Compliance enforcement
In short, document management helps you manage documents, while document control ensures those documents are correct, approved, and compliant.
Capture Key Data from Your Documents Easily
Use Docparser to automate data entry, save time, and streamline your document-based workflows.
No credit card required.
What Are the Components of Document Control?
An effective document control system relies on several core components working together to keep documents accurate, traceable, and compliant throughout their lifecycle. Here’s a brief overview of each component.
Component | Definition |
Document number | Each controlled document is assigned a unique identifier. Document numbers make it easy to track, reference, and retrieve documents while avoiding confusion between similar files or records. |
Version control | Document version control ensures that only the latest, approved version of a document is in use. It tracks changes over time, prevents outdated versions from circulating, and provides visibility into what was modified and when. |
Audit trail | An audit trail records every action taken on a document, from creation to edits, approvals, and access. This is crucial for accountability and verifying compliance during internal or external audits. |
Periodic review of documents | Reviewing documents periodically confirms their accuracy and relevance. It also helps identify obsolete information and update documents when necessary to align with current processes and regulations. |
Access control | Access control defines who can view, edit, approve, or delete documents. It reduces the risk of unauthorized changes or data exposure. |
Change control | Change control establishes a standard process for requesting, reviewing, approving, and documenting changes. This ensures updates are intentional, traceable, and communicated clearly to all stakeholders. |
Why Is Document Control Important?
Without document control, there will be chaos. Crucial information will be lost during verbal communications or in a sea of emails when it’s not documented and approved. Employees might share outdated documents or inadvertently leak sensitive information. Others might not be able to perform their tasks and meet deadlines because they can’t find the current versions of the documents they need.
And then there is the risk of non-compliance. When ISO audits reveal obsolete documents (for example, product specifications, SOPs, training reports, etc.), the company faces the risk of losing its certification and must take corrective action immediately.
Here are the key benefits of document control:

- Faster retrieval: Controlled documents are clearly labeled, versioned, and stored in a consistent structure, making it easy to find the right document quickly without searching through outdated files.
- Better collaboration: Teams can work together with confidence, knowing they are viewing the same approved version. Defined roles and permissions reduce confusion and prevent conflicting edits.
- Audit readiness: With complete audit trails, version histories, and approval records, organizations can respond to audits without scrambling to locate documents or justify changes.
- Improved compliance: Document control helps enforce regulatory requirements, internal policies, and quality standards by ensuring documents are reviewed, approved, and updated on a regular basis.
How to Implement Document Control
Implementing document control starts with defining clear rules for how documents are created, reviewed, stored, and updated. The steps below outline how to put your document control system in place:
- Identify all the documents that must be controlled.
- Assign a document control specialist who is responsible for approving and monitoring documents. That person will have access to a centralized repository where documents are stored.
- Standardize naming conventions. This makes it easy to search for documents and differentiate versions of any given document — essential during audits!
- Set standard procedures for access permissions, document version control, and change tracking. These procedures prevent unauthorized edits and outdated documents from circulating. You implement and enforce them with your document control software.
- Design approval workflows that route documents to the right reviewers, track approval status, and ensure only approved versions are shared.
- Define which tools teams will use to collaborate and co-author documents.
- Leverage automation tools to automate simple but repetitive tasks that consume time and may cause errors when done manually.
- Schedule and conduct regular review cycles to keep documents accurate and compliant.
- Establish a procedure for archiving old or outdated documents. This allows you to remove these documents from circulation while still keeping them accessible for future reference or compliance. You should also set a policy for deleting documents.
- Finally, prepare adequate training so that teams learn the importance of document control and how to follow the standard operating procedures.
These Industries Benefit Massively from Document Control Systems
While document control systems are valuable across many sectors, some industries heavily depend on them due to strict regulations, complex workflows, and high compliance requirements.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations manage sensitive patient records, policies, and clinical documentation. The stakes are higher than in other industries: information must be accurate, secure, and accessible at all times. Needless to say, regulations and audit requirements can be very strict.
Pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutical companies must maintain strict control over research documents, manufacturing records, and quality documentation – particularly SOPs. In addition to improving efficiency and complying with ethical and regulatory standards, document control systems also help retain knowledge and protect patient data, intellectual property, and in-house research.
Legal services
Law firms handle large volumes of contracts, case files, and confidential records. Document control plays a critical role in preventing the use of outdated or incorrect documents, which can have devastating consequences. Productivity takes a nose dive, but what’s even worse is using those documents in a case, leading to sanctions, malpractice claims, and reputational damage. Therefore, document control systems are necessary.
Engineering and construction
Engineering and construction projects depend on precise drawings, specifications, and change orders. Document control helps teams manage revisions, coordinate across stakeholders, and avoid costly errors caused by outdated or incorrect documentation. Proper control helps prevent rework, schedule overruns, and cost escalation.

In Conclusion
The way organizations handle documents plays a major role in their operational efficiency. Beyond organizing files, document control ensures that authorized personnel work with the right version of any given document, all while keeping a clear track record of its history. As a result, teams collaborate without confusion or errors, and organizations stay audit-ready.
Adding document parsing to the equation can help you create documents with accurate and organized data. Tools like Docparser, combined with document control software, can automatically extract data from structured, semi-structured, or unstructured documents and export it where you need it to be. For example, your accounting system can generate reports populated with data from invoices or bank statements. If manual data entry is hampering your document control system, try parsing documents with Docparser to save time and create documents ready to be approved and used.
Capture Key Data from Your Documents Easily
Use Docparser to automate data entry, save time, and streamline your document-based workflows.
No credit card required.




